To start with, what not to do after eye dilation?
Avoid driving after your exam, spend a lot of time in bright light, relax in the sun, and try to read small fonts…
To wear as you leave the eye doctor’s office, you will be given some enormous disposable sunglasses. By doing this, sun damage to the eyes will be reduced. Your pupils naturally constrict to protect your eyes when the sun is bright, but when your eyes are dilated at the doctor’s office, they are unable to do so. So, until your pupils return to normal, you need to exercise extra caution outside in the sun.
Continue reading to learn more about what to avoid doing if your eyes have dilated.
Table of Contents
About Eye Dilation
Your eyes may be dilated by the optometrist during an eye exam so they can examine the structures at the back of your eye. They are looking for anomalies that could be symptoms of the following conditions:
- High blood pressure: If high blood pressure is left untreated, especially over an extended period of time, the retina’s blood vessels may sustain damage.
- Retinal detachment: This is a reference to the retina separating from the blood vessels that are connected to it. The retina consequently receives insufficient nutrients and oxygen.
- Diabetes: The development of diabetic retinopathy is a possibility for those with diabetes, particularly if long-term high blood sugar levels are not managed. The retina’s blood vessels are impacted by this condition.
- Macular degeneration: The macula portion of the retina is damaged in this condition. In some cases, it can lead to permanent vision loss.
- Glaucoma: The optic nerve can be harmed by several types of glaucoma. The damage is typically caused by abnormally high eye pressure.
To look for an acute injury, such as a retinal detachment, eye dilation may be performed as part of a thorough eye examination. Whatever the cause, dilation is carried out in the same way. Your pupils will enlarge as a result of the eye drops the doctor inserts.
Your need to have your pupils dilated will depend on a number of variables. Only if you regularly have eye exams and are in generally good health could your doctor advise it. The following factors could alter the regimen your doctor advises:
- You are older than 60.
- You’ve experienced retinal detachments or other conditions that affect the structures in the back of your eye in the past.
- There are new symptoms in your eyes.
- You have a higher risk of developing glaucoma if you’re Hispanic or African American.
- You suffer from diabetes or another condition that could harm your eyes.
What Not To Do After Eye Dilation?
You should take extra care after having your eyes dilated in addition to refraining from driving.
- Avoid staring at electronic devices: Digital eye strain may be caused by the blue light that is emitted by electronic screens. Reduce the amount of time you spend on screens and the amount of blue light you are exposed to until your pupils are back to normal.
- Refrain from attempting to read small fonts: Your vision will be hazy after the eye is dilated. It is possible to read small print in a book or on your phone, but doing so while trying to see clearly could result in eye strain, fatigue, and headaches.
- Avoid spending too much time in the sun. Avoid looking directly at the sun because it can harm your eyes. This is even more critical to keep in mind after dilation. In order to reduce the likelihood of UV damage, your pupils will typically automatically constrict (get smaller) in bright light. However, after a dilated eye exam, your eyes are unable to use this built-in defense mechanism.

What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Eye Dilation?
Because our eyes are our windows to the world, it can be a little disconcerting when they’re not “right.” Knowing what symptoms to anticipate can help you feel less anxious about the procedure because you will know what side effects to attribute to it. More importantly, you’ll be aware that they aren’t serious or long-lasting and that they will go away.
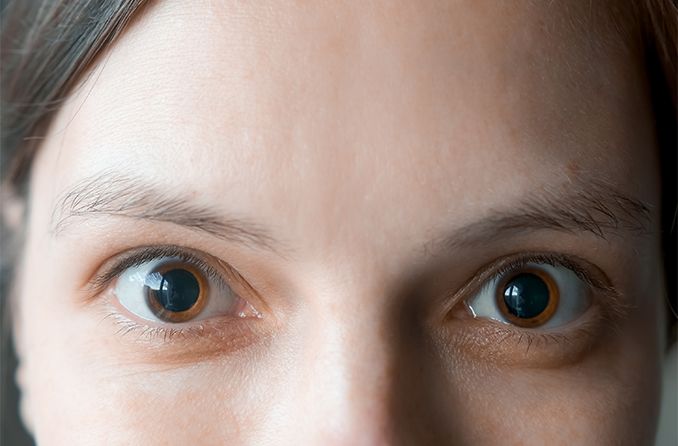
In the initial moments after dilation, some people may feel a stinging in their eyes. This is most likely to happen as the drops are applied, and it shouldn’t continue for the duration of the procedure.
Additionally, you might have trouble focusing on nearby objects and have blurry vision. Until the drops wear off and your pupils can once again respond appropriately to light, you will probably experience light sensitivity.
How Long Does Eye Dilation Last?
Your eye doctor most likely won’t be able to pinpoint the precise duration of the dilation. This is due to the fact that it differs between patients.
Your eyes may enlarge more quickly depending on the amount of melanin in your irises, which determines the color of your eyes. Your eyes will widen more quickly if they are a lighter color, like blue or green. It will take a little longer if your eyes are darker and your iris contains more melanin.
The duration of dilation is typically 4 to 6 hours. You will continue to experience some or all of the above-mentioned symptoms during that time. Although it is uncommon, some patients’ dilation may last longer than six hours.
Since there isn’t really a way to make eye dilating go away more quickly, it’s best to wait it out and try not to get anxious. Contact your eye doctor if the length of time it is taking for dilation to pass concerns you.
Why Is It Necessary To Dilate Our Eyes?
Your eyes can be seen more clearly by your eye doctor thanks to dilation in some areas. Your eye doctor can examine the interior and exterior of your eye using a magnifying lens after dilation of your pupils.
How does this matter? To diagnose some conditions affecting the health of the eyes, eye doctors must examine the retina, blood vessels, optic nerve, and other components of the inner and posterior eye. Over time, these problems will affect your vision, and in some cases, identifying them early can aid in the diagnosis of other health issues.
Glaucoma
The part of your eye that communicates visual information to your brain is called the optic nerve. To put it another way, we depend on it to interpret what we see and ultimately to see anything at all.
The optic nerve can be harmed by glaucoma, which is typically brought on by high eye pressure. More damage can be stopped the sooner it is discovered. Glaucoma will impair vision and could even result in blindness if left untreated.
Retinal Detachment
We often take vision for granted, but a lot has to happen for you to “see” what’s in front of you! Light first enters the eye, where it is focused by your lens onto your retina. The retina and optic nerve work together to translate images into signals that the optic nerve can send to the brain.
The retina can become detached from the back of your eye, which is known as retinal detachment. The retina and optic nerve’s connection has thus been severed, according to this. You may lose some or all of your vision, depending on how much of the retina has separated from the back of your eye.
Macular Degeneration
Age plays a major role in macular degeneration, which is more likely to affect people 65 and older. Damage to the retina is typically the result of deposits accumulating beneath the macula. There are times when abnormal blood vessel development in that region contributes to macular degeneration.
Even though macular degeneration does not result in total blindness, it is still very frustrating! Your central vision will be impaired even though you’ll still have some vision. In other words, you’ll be able to see out of the corner of your eye, but it will be challenging to impossible to see what’s directly in front of your eye.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Type 1 or type 2 diabetes and high blood sugar together lead to diabetic retinopathy. Some patients’ medical diagnoses of diabetes have even been aided by the detection of retinopathy!
Blood vessels may become damaged and start to leak fluid into the eye in the early stages. This could result in the retina swelling. The retina will develop new, abnormal blood vessels that travel to the eye’s center in more advanced or severe cases of retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy will get worse and may lead to blindness if untreated.
When Should We Begin Having Our Eyes Dilatation?
The majority of eye doctors advise starting general eye exams in childhood, but not all eye exams include dilation. So when should you talk to your ophthalmologist about dilation?
When you should begin having your eyes dilated depends on a number of different factors. If you haven’t had your eyes dilated by the time you turn 60, you should start getting them done every year. Nevertheless, depending on your health and even your ethnicity, you might need to start sooner.
You should get an annual dilation if you’ve ever experienced eye problems, such as retinal detachment or ongoing problems like glaucoma. Additionally, if you suffer from conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure that could harm your eyes, this is also true.
If you are African American or Hispanic, you are more likely to develop glaucoma and should start dilation around the age of 40.
Last but not least, if your eye doctor notices something during a routine eye exam that causes them concern, you should follow their advice and let them dilate your eyes. Make plans for a follow-up appointment if you are not prepared for the procedure that day.
In What Ways Can We Get Ready For Eye Dilating?
A few pre-procedure suggestions will help the procedure and recovery from eye dilation go more smoothly.
Find a doctor you feel comfortable with after doing some research! Although eye dilation can be performed by any licensed eye doctor, it doesn’t hurt to work with someone who makes you feel safe and secure.
Make arrangements for a ride home to begin with. We don’t recommend trying to drive after having your eyes dilated because you might find it unsettling the first few times, even though some people find it to be comfortable. Have a family member or friend drive you to and from your appointment, or make arrangements to have a hired car pick you up.
Bring sunglasses and possibly a baseball cap whether or not you decide to drive! If it’s a sunny day, you might find the light jarring and giving you headaches. Your fear of light will subside if you give yourself some cover and darkness.
Until your eyes are back to normal, if you typically wear contacts, think about sticking with your glasses. Contact lenses after dilation may be uncomfortable, even though there are no risks involved.
Plan some downtime for the hours after surgery, too. Avoid bright TVs, computers, and even print because doing so can strain your eyes.

What Negative Effects Can Eye Dilating Drops Cause?
Although dilation has temporary negative side effects, it is safe over the long term. They typically last for four to six hours.
Dilation may have negative effects, such as:
- light sensitivity
- blurry vision
- trouble focusing on close objects
- stinging right after the drops are put in
Until the dilation drops wear off, you might not be able to wear contact lenses.
Tips For Managing Eye Dilation Side Effects
It’s crucial that you look after your eyes and yourself after your appointment because dilation can lead to blurry vision and light sensitivity.
- Have a friend or member of your family drive you home after your appointment, or use a taxi. When experiencing dilation, many people choose to drive themselves home if they feel confident doing so.
- After your appointment, bring sunglasses to protect your eyes. Your eyes could be damaged by the sun. Bringing your own sunglasses never hurts, even though your doctor’s office might provide them after dilation.
- If you can, take a few hours off of work. It’s crucial to avoid straining your eyes while reading, even though it might be difficult.
How Eye Dilation Affects Your Vision?
Your doctor will use specialized drops to widen your pupils before dilating of the pupils. In order to check for disease symptoms, they can now see your entire eye, including all of the nerves and blood vessels at the back.
The duration of the drops your doctor uses ranges from 4-6 hours, occasionally even longer. Thus, instead of closing up to block out light in bright environments as they normally would, your pupils remain open. Your vision becomes hazy as a result of the glare. If you decide to drive before the drops have worn off, you won’t be able to see things as clearly as usual and it will seem much brighter than usual, especially outside in the sunlight.
Read about: Can You Drive With Dilated Eyes?
What Illnesses Are Visible With Eye Dilation?
Our eyes also deteriorate with age. As a result, conditions like retinopathy, macular degeneration, and glaucoma can develop. A dilated eye exam is recommended for most adults once a year. The doctor can see more clearly after dilation in the following areas of the eye that are more susceptible to damage: the macula, the retina, and the optic nerve.
- Diabetic Retinopathy – occurs as a result of abnormal blood vessel growth, swelling, and blood vessel leakage in the retina. If unattended, a person’s vision may become blurry or distorted, and eventually, blindness may set in.
- Macular Degeneration – This is typically brought on by deposits building up beneath the retina and/or abnormal blood vessel growth, both of which are related to damage to the retina. Although macular degeneration cannot be cured, there are treatments that your doctor may suggest that could halt the disease’s progression.
- Glaucoma – Damage to the optic nerve is the cause of this. Due to the slow progression of glaucoma, there are typically no symptoms, but a dilated eye exam can easily identify the disease. Glaucoma may cause irreversible blindness if left untreated.
The doctor can identify these conditions in their early stages by performing routine dilated eye exams. Before significant harm is done, treatment can be started to stop or slow the disease’s progression. See more about How To Put In Eye Drops
How Long Does It Take for Your Eyes to Settle?
Depending on your age, the medication you may be taking, the color of your eyes, and how long it takes for them to settle and return to normal, it may take longer. You should allow at least four to six hours, and possibly more, for your pupils to return to normal. It’s best to prepare in advance to avoid feeling anxious while having your eyes dilated. Use the time you have to rest to your advantage!
FAQs
Why Is Using A Phone After Eye Dilation Bad?
After being dilated, your eyes become much more sensitive to light, particularly sunlight. In addition, the blue light emitted by smartphones and other digital screens can make your eyes strain even more. To avoid wearing out and discomforting your eyes, try to limit the amount of time you spend on your phone until your pupils return to normal. Even though it might be challenging, you should put your eye health before anything else. Furthermore, you might think it’s kind of nice!
How Long Does It Take For Your Eyes To Adjust?
Depending on your age, the medication you may be taking, the color of your eyes, and how long it takes for them to settle and return to normal, it may take longer. Your pupils will return to normal in at least four to six hours, and possibly longer. Make preparations in advance to make having your eyes dilated less stressful. Use the time you have to rest wisely!
How Soon After Eye Dilation Can You Drive?
You can resume driving if you don’t experience any side effects that impair your vision. When these effects, such as blurriness or difficulty focusing on objects, occur, it is typically advised that you avoid driving.
If it’s your first time having an eye examination with dilation, make arrangements to be picked up by a ride since you don’t yet know how the procedure will affect you. By doing this, you can be sure that you are ready in the event that your vision is seriously impaired and you cannot safely drive yourself home.
What Is Eye Dilation As A Treatment?
Certain eye conditions, like lazy eye and eye inflammation, may be helped by dilation of the pupils. The same eye drops that are used to dilate your eyes during an examination are also used as a treatment. It follows the same general procedure.
Dilation is typically performed as part of a thorough eye examination. A possible eye injury may also be assessed in a crisis situation.
Eye Dilation Costs
Eye dilation is typically covered by the overall cost of a comprehensive eye exam, which ranges from $50 to $150 in the absence of insurance.
Dilation typically costs between $30 and $50 when billed separately.
Conclusion
Therefore, do you know what not to do after eye dilation? You must keep it in mind.
The side effect of eye dilation is blurry vision, which may be the most annoying one. On the phone or computer, trying to read a book or a letter can be aggravating, tire your eyes, and give you headaches. Before concentrating on the fine print, give your eyes some time to return to normal. After getting your eyes dilated, returning to work or school might not be the best choice for you.